内容|SAP Hybris Commerce的安装脚本内容解析

文章图片
(1) Setup = Invoked by default if no task is specified with install command. It installs recipe & copies files.
(2) Initialize = Initializes the recipes application.
(3) Start = Start the application.
https://www.novusedu.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/4-Hybris-Install.pdf
在recipe文件夹里看到的build.gradle内容里包含的setup任务: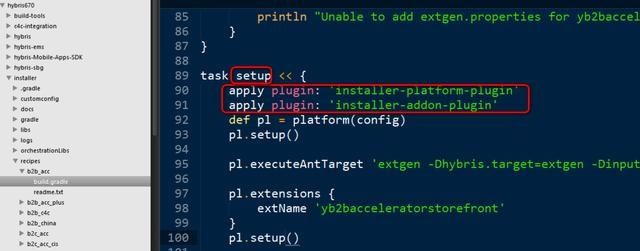
文章图片
使用的两个plugin:
* installer-platform-plugin
* installer-addon-plugin
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/32352816/what-the-difference-in-applying-gradle-plugin#:~:text=The%20plugins%20block%20is%20the%20newer%20method%20of,method%20of%20adding%20a%20plugin%20to%20your%20build.
两种声明plugin使用的方式:
文章图片
```groovy
apply plugin: 'someplugin1' apply plugin: 'maven'
and other one:
plugins { id 'org.hidetake.ssh' version '1.1.2' }
```
> The plugins block is the newer method of applying plugins, and they must be available in the [Gradle plugin repository](https://plugins.gradle.org/). The apply approach is the older, yet more flexible method of adding a plugin to your build.
The new plugins method does not work in multi-project configurations (subprojects, allprojects), but will work on the build configuration for each child project.
区别在于后者的语法要求声明的plugin必须在gradle plugin repository里可用:
> Keep in mind, that applying a plugin using the plugins DSL (plugins {...}) does not work for your private plugins or company plugins which are not published to the official Gradle plugin repo. That's why I hope the old approach will at least survive until the new one does support searching in private repositories.
# plugin的定义
> Gradle at its core intentionally provides very little for real world automation. All of the useful features, like the ability to compile Java code, are added by plugins. Plugins add new tasks (e.g. JavaCompile), domain objects (e.g. SourceSet), conventions (e.g. Java source is located at src/main/java) as well as extending core objects and objects from other plugins.
给一个Gradle项目应用plugin,可以扩展该project的功能:
(1) Extend the Gradle model (e.g. add new DSL elements that can be configured)
(2) Configure the project according to conventions (e.g. add new tasks or configure sensible defaults)
(3) Apply specific configuration (e.g. add organizational repositories or enforce standards)
# plugin的类型
There are two general types of plugins in Gradle, binary plugins and script plugins - 分为二进制插件和脚本插件两类。
Binary plugins are written either programmatically by implementing Plugin interface or declaratively using one of Gradle’s DSL languages. Binary plugins can reside within a build script, within the project hierarchy or externally in a plugin jar.
Script plugins are additional build scripts that further configure the build and usually implement a declarative approach to manipulating the build. They are typically used within a build although they can be externalized and accessed from a remote location.
https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/plugins.html
# plugin的解析
> Resolving a plugin means finding the correct version of the jar which contains a given plugin and adding it the script classpath. Once a plugin is resolved, its API can be used in a build script.
一旦插件解析成功之后,在build script内可以使用其API.
Script plugins are self-resolving in that they are resolved from the specific file path or URL provided when applying them. - 脚本插件是自动解析的。
Core binary plugins provided as part of the Gradle distribution are automatically resolved. Gradle发行版里自带的核心二进制插件自动被解析。
再回过头来看Hybris recipe文件夹下的build.gradle的三个任务:
setup任务使用了插件installer-platform-plugin的setup方法:
推荐阅读
- 综艺|《街舞3》选手质量两极分化,内容注水,9.0高分还能保持多久?
- 购物袋|明年起禁用不可降解塑料购物袋,具体内容揭秘有哪些影响
- 文旅|快手发布文旅光合计划,百亿流量鼓励优质文旅内容生产
- 直播|小红书:二季度拦截刷量1.3亿次,三季度重点规范提升直播内容
- 文章|网站内容该如何更新,怎么让文章快速收录?
- 双星|科学家发现神奇的异类双星系统
- 用户上传内容侵权,网络平台责任如何厘清
- 内容|赵丽颖给包包贴创可贴,看见被覆盖的内容后,可真是一个小机灵鬼
- 兼任|奈飞敲定CEO接班人:宣布首席内容官兼任联席CEO
- 日本|千叶雄大陷入40万公里宇宙级恋爱,田村淳介绍日本最新流行内容













